
Breast cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the breast. It can start in one or both breasts. It occurs almost entirely in women, but men can get breast cancer, too.
Cancer starts when cells begin to grow out of control.
It’s important to understand that most breast lumps are benign and not cancer (malignant). Non-cancer breast tumors are abnormal growths, but they do not spread outside of the breast. They are not life threatening, but some types of benign breast lumps can increase a woman’s risk of getting breast cancer.
Any breast lump or change needs to be checked by a health care professional to find out if it is benign or malignant (cancer) and if it might affect your future cancer risk. See Non-cancerous Breast Conditions to learn more.
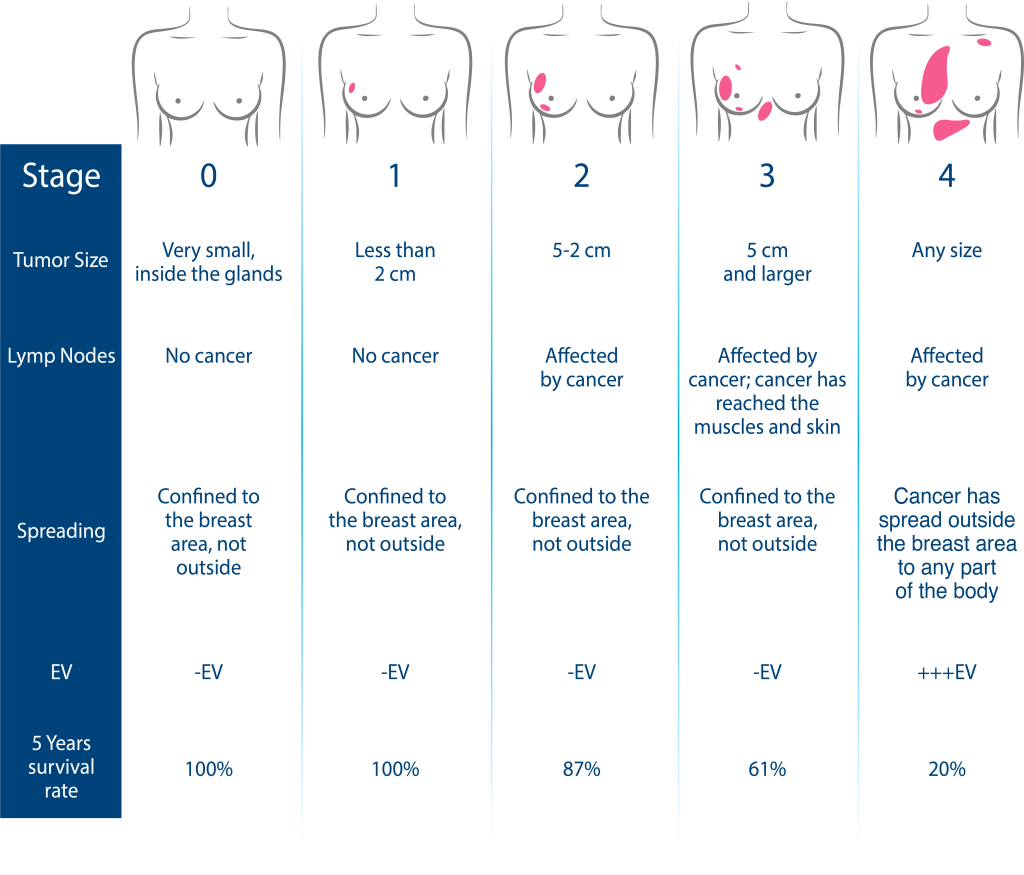
Stages of Breast Cancer
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of breast cancer include:
- A new lump or thickening in or near the breast or in the armpit
- A change in the size or shape of the breast
- A dimple or puckering in the skin of the breast. It may look like the skin of an orange
- A nipple turned inward into the breast
- Nipple discharge other than breast milk. The discharge might happen suddenly, be bloody, or happen in only one breast
- Scaly, red, or swollen skin in the nipple area or the breast
- Pain in any area of the breast.
Who are in risk?
The factors that raise your risk of breast cancer include:
- Older age
- History of breast cancer or benign (noncancer) breast disease
- Inherited risk of breast cancer, including having BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene changes
-
Dense breast tissue
A reproductive history that leads to more exposure to the estrogen hormone, including:
• Menstruating at an early age
• Being at an older age when you first gave birth or never having given birth
• Starting menopause at a later age - Taking hormone therapy for symptoms of menopause
- Radiation therapy to the breast or chest
- Obesity
- Drinking alcohol
- Having a genetic syndrome
- Having a family history
